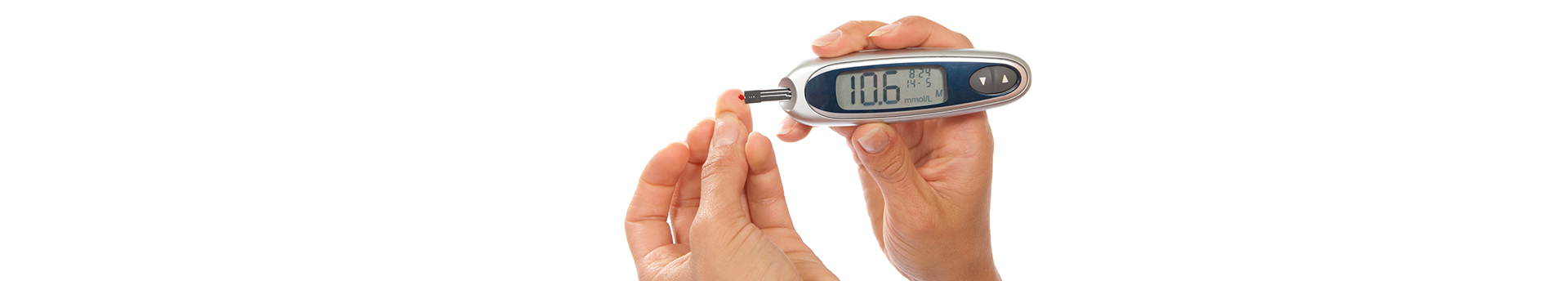
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus refers to a group of diseases that affect how your body uses blood sugar (glucose). Glucose is vital to your health because it's an important source of energy for the cells that make up your muscles and tissues. It's also your brain's main source of fuel.
The underlying cause of diabetes varies by type. But, no matter what type of diabetes you have, it can lead to excess sugar in your blood. Too much sugar in your blood can lead to serious health problems.
Chronic diabetes conditions include type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Potentially reversible diabetes conditions include prediabetes — when your blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes — and gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy but may resolve after the baby is delivered.
Diabetes symptoms vary depending on how much your blood sugar is elevated. Some people, especially those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, may not experience symptoms initially. In type 1 diabetes, symptoms tend to come on quickly and be more severe.
Some of the signs and symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes are:
Increased thirst
Frequent urination
Extreme hunger
Unexplained weight loss
Presence of ketones in the urine (ketones are a byproduct of the breakdown of muscle and fat that happens when there's not enough available insulin)
Fatigue
Irritability
Blurred vision
Slow-healing sores
Frequent infections, such as gums or skin infections and vaginal infections
Type 1 diabetes can develop at any age, though it often appears during childhood or adolescence. Type 2 diabetes, the more common type, can develop at any age, though it's more common in people older than 40.